| maximum number of live births per donor | ¡@ | average number of natural children per donor = fertility rate | average number of children per donor in one pregnancy |
| k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes:
(1) Variables in red need to be assigned based on demographic and medical data from the area of interest.
(2) Variables in blue are default values. They can be changed if more information becomes available. However, different values do not seem to affect the results much.
(3) After users assign values for variables in red, the resulting Y, F, or increased incidence will be changed. User can then create a plot for various k's and the corresponding resulting values.
(4) Reference of the calculation is Wang et al. (2006), Maximum Number of Live Births per Donor in Artificial Insemination.
----- Created by Charlotte Wang in Aug, 2006. -----
¡@
| maximum number of live births per donor | ¡@ | average number of natural children per donor = fertility rate | average number of children per donor in one pregnancy |
| k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
¡@
|
number of potential marriages
between offspring and relatives ( |
|||
| half sibling | biological father or mother | uncle-nice or aunt-nephew | half uncle-nice or half aunt-nephew |
|
|
|
|
|
| first cousin | half first cousin | first cousin once removed | half first cousin once removed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
¡@
| the chance that a newborn will ever reproduce | the factor of assortive mating for age | the factor of assortive mating for phenotype | the factor of assortive mating for geographical location | average number of newborns in a year |
| l |
|
C | Q | A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
¡@
| number of donors per year | success rate | number of potential marriages between offspring and relatives | probability of mating |
| D | S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
¡@
Result 1: Number of Consanguineous Mating per Year
| number of consanguineous mating per year |
|
|
|
|
¡@
Result 2: Average Level of Coefficient of Inbreeding in Population with AID
| the original coefficient of inbreeding existing in the population | number of marriages per year |
| F0 | M |
|
|
|
| ¡@ | ¡@ |
| average level of coefficient of inbreeding in population with AID | |
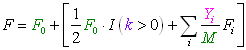 |
|
|
|
|
¡@
Result 3: Average Level of Coefficient of Inbreeding in Population with AID
| ¡@ | autosomal recessive hereditary disease | autosomal dominant hereditary disease | complex disease | |
| number of 15 to 44-year-old people | prevalence | prevalence | prevalence | |
| ¡@ | ¡@ | penetrance | probability of a disease child | |
| given one ill parent | given two ill parents | |||
| increased incidence due to AID per 1,000,000 people | increased incidence due to AID per 1,000,000 people | increased incidence due to AID per 1,000,000 people | ||
¡@